Projects
Overview
These projects were comprehensive team efforts, where I was often the team leader.They mainly focus on urban transportation and environmental issues, employing methods such as multi-agent systems, deep learning and reinforcement learning to achieve prediction, simulation and optimization, providing insights for urban planning and policy.
▶ Current work at Spatial Pleasure
Sep 02, 2024 – Present
I work remotely at 0.6 FTE per month as a data scientist with main tasks regarding processing and integrating traffic data, developing traffic simulation models and optimization systems.
In many ways, the work here is more akin to research, as the projects require strong knowledge of mathematical statistics and involve exploratory methods. I look forward to collaborating with the company's lab to publish the outcomes of our projects if the opportunity arises.
Currently, I am primarily responsible for two projects:
1 Origin-Destination Estimation in Sapporo
We use the four-step model of trip generation, trip distribution, mode choice and route assignment to predict traffic demand and identify key factors, offering insights on public transit capacity allocation.
- Leverage GTFS, IC card, and socioeconomic data to perform spatiotemporal clustering of O-D trips
- Incorporate environmental factors (e.g., carbon emissions, noise pollution) into the model to enhance the sustainability of public transportation
- Utilize machine learning algorithms to perform data-driven modeling without predefined assumptions and
- ......
2 Multi-Agent Transport Simulation in Tyoko
The four-step model relies on aggregated data, limiting its ability to reflect individual travel decisions while agent-based models can compensate for this.
- Introduce new transport modes (e.g., autonomous driving, shared mobility) into the traffic simulation
- Model heterogeneity in agent behavior (e.g., income and age) by differentiating utility functions
- Integrate the influence of behavioral psychology on the rational agent (e.g., acceptability of autonomous vehicles)
- ......
▶ Optimizing electric vehicle charging station placement using reinforcement learning
June 20, 2024 – Aug 15, 2024
Keywords: electric vehicle charging station, location selection, reinforcement learning, spatial optimization
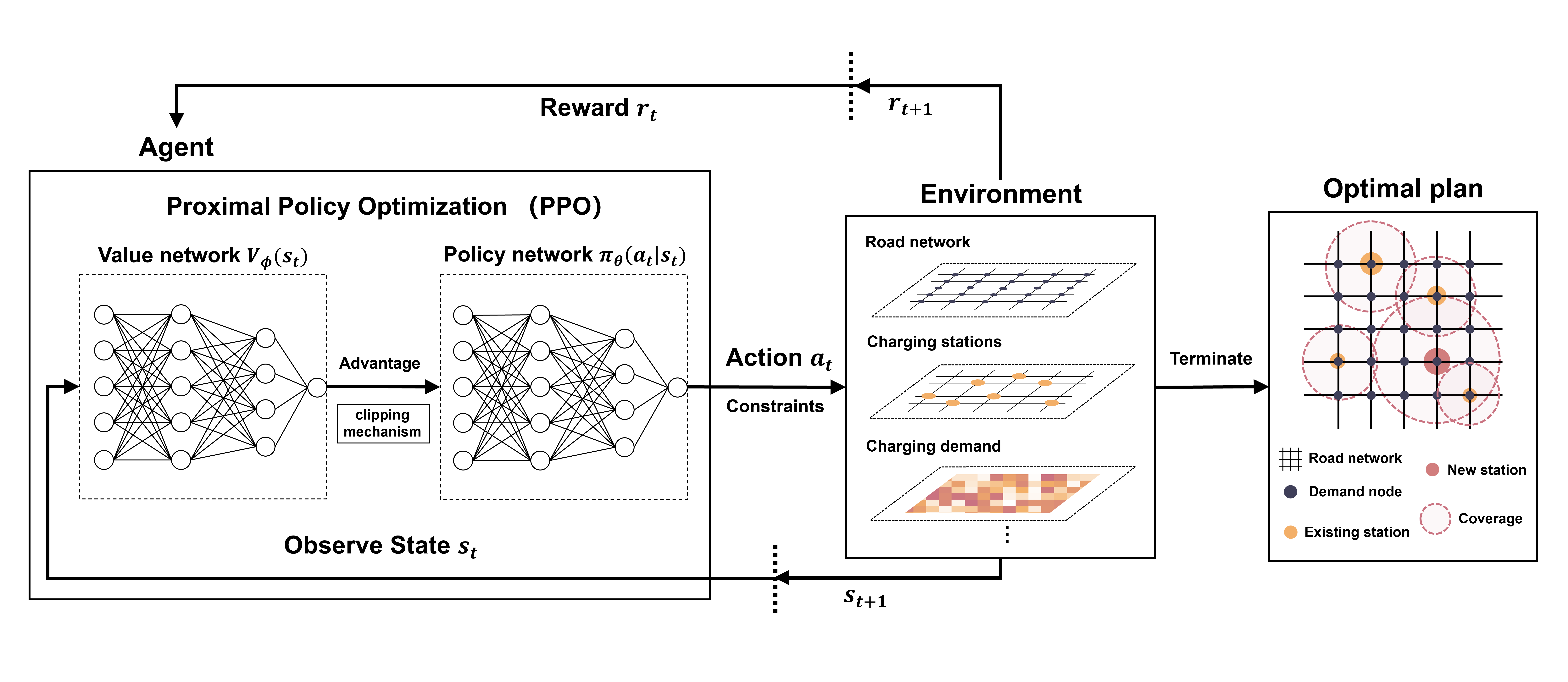
Project framework
Iterative optimization of utility by different RL algorithms
The optimal charging station placement by DQN algorithm
Optimizing electric vehicle charging station placement is key to implementing zero-emission policies in central London. Using open charge map data, the study framed the problem as a reinforcement learning task, where the agent learns to take optimal actions by adjusting its strategy based on feedback. This results in a deployment that balances coverage benefits and time costs within budget constraints, maximizing overall utility.
Components of the RL problem
- State: The current spatial layout of charging stations and charger configuration.
- Action: Adding new charging stations, increasing the capacity of existing stations, or relocating stations.
- Reward: The difference in total utility before and after each layout modification.
- Algorithms: Deep Q-learning Network (DQN), Advantage Actor-Critic (A2C) and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO).
As a result, reinforcement learning algorithms show significant improvements over traditional methods, with the DQN-based layout performing best across metrics. Each algorithm offers unique strengths: DQN minimizes travel time in high-demand areas, A2C improves overall service balance, and PPO enhances charging efficiency at existing stations.
Honor: High distinction (96/100) in course ST455 Reinforcement Learning
Preprint forthcoming on arXiv. Notebook. Code available on GitHub.
▶ Disentangling associations between socio-environmental dynamics and subjective well-being during and after COVID-19
Feb 01, 2023 – Aug 25, 2023
Keywords: subjective well-being, neighborhood resilience, COVID-19, explainable machine learning, social media data
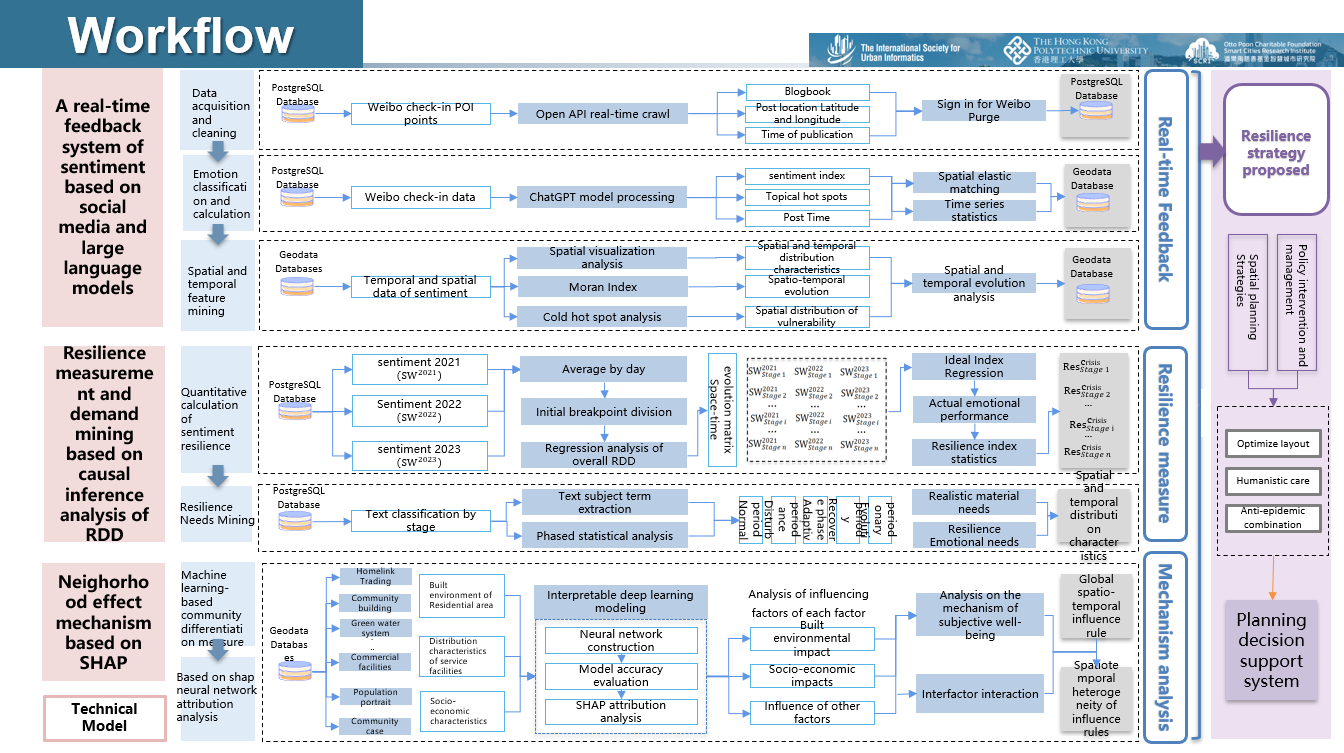
Project framework and workflow
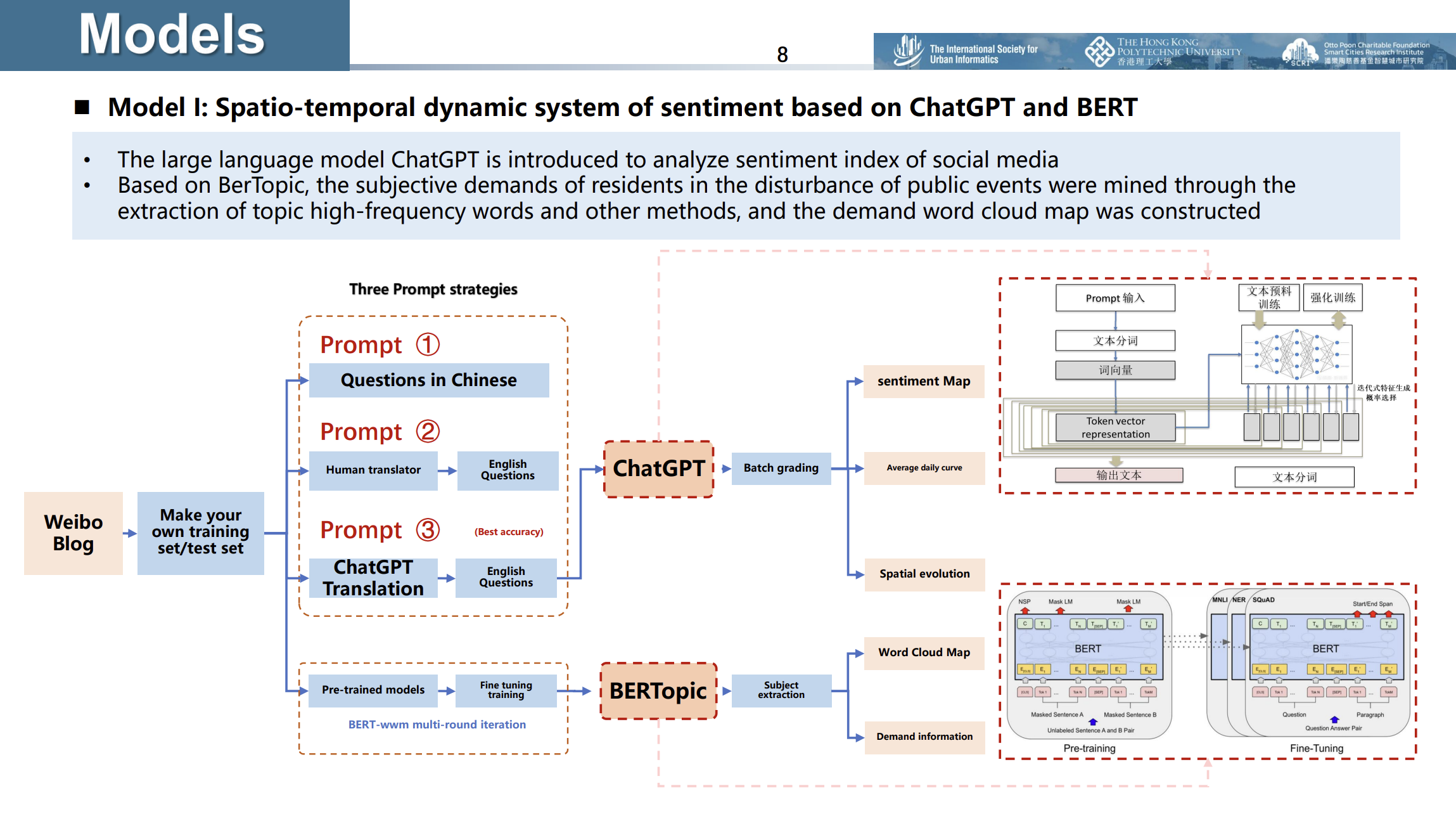
Spatiotemporal SWB extracted by ChatGPT and BERT
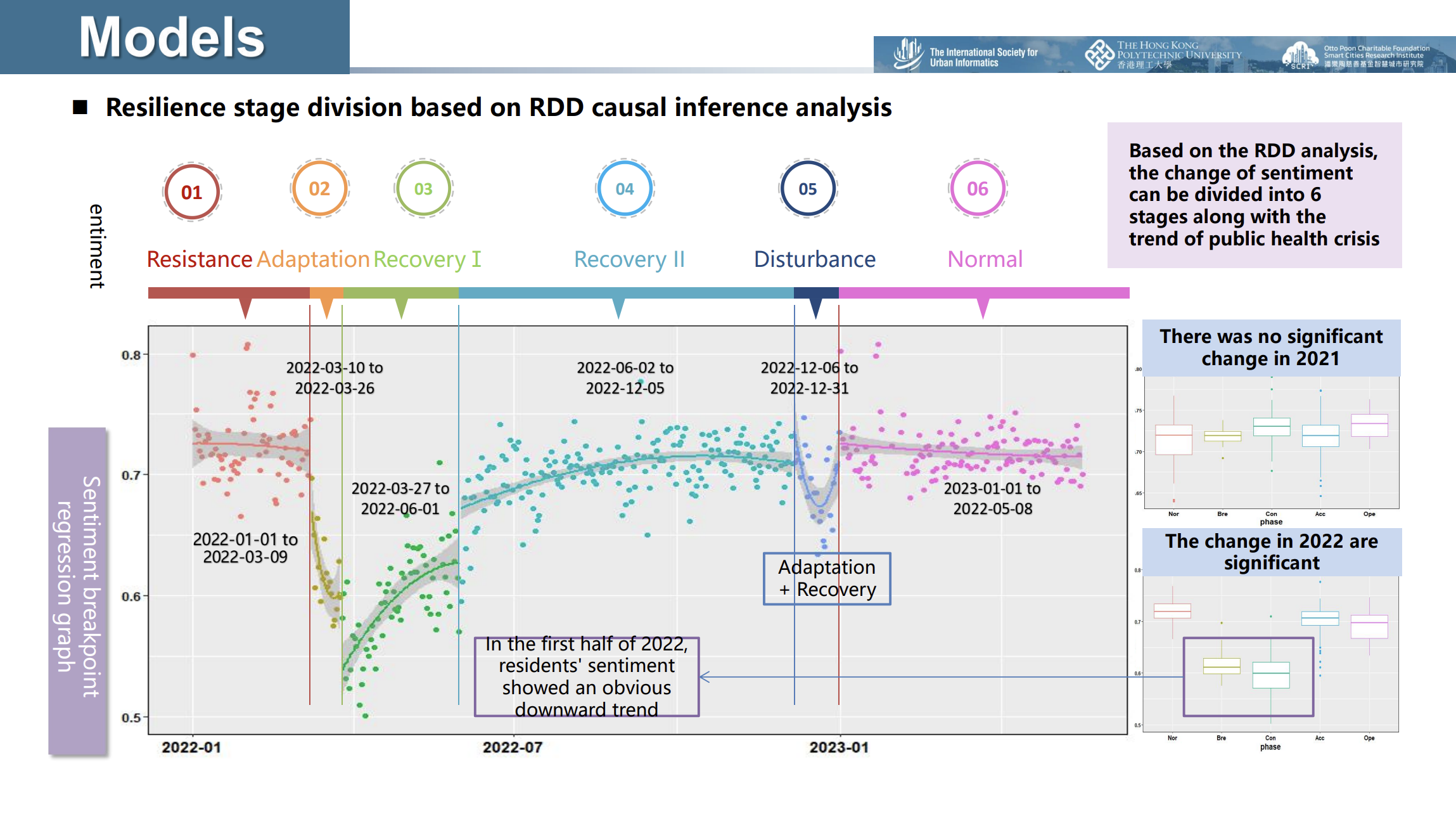
Resilience stage division by Regression Discontinuity Design
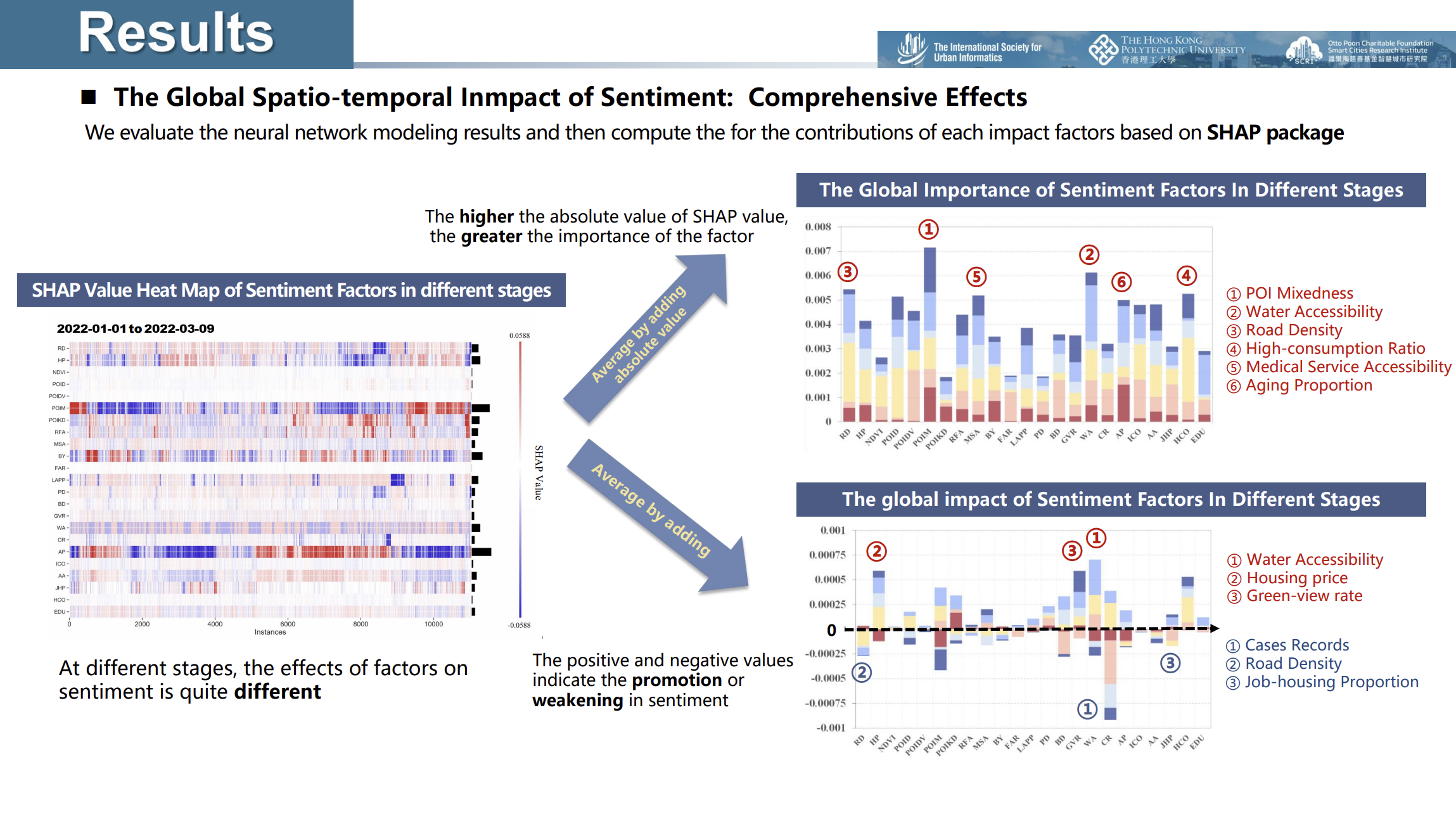
The Global Spatiotemporal impact of SWB using SHAP
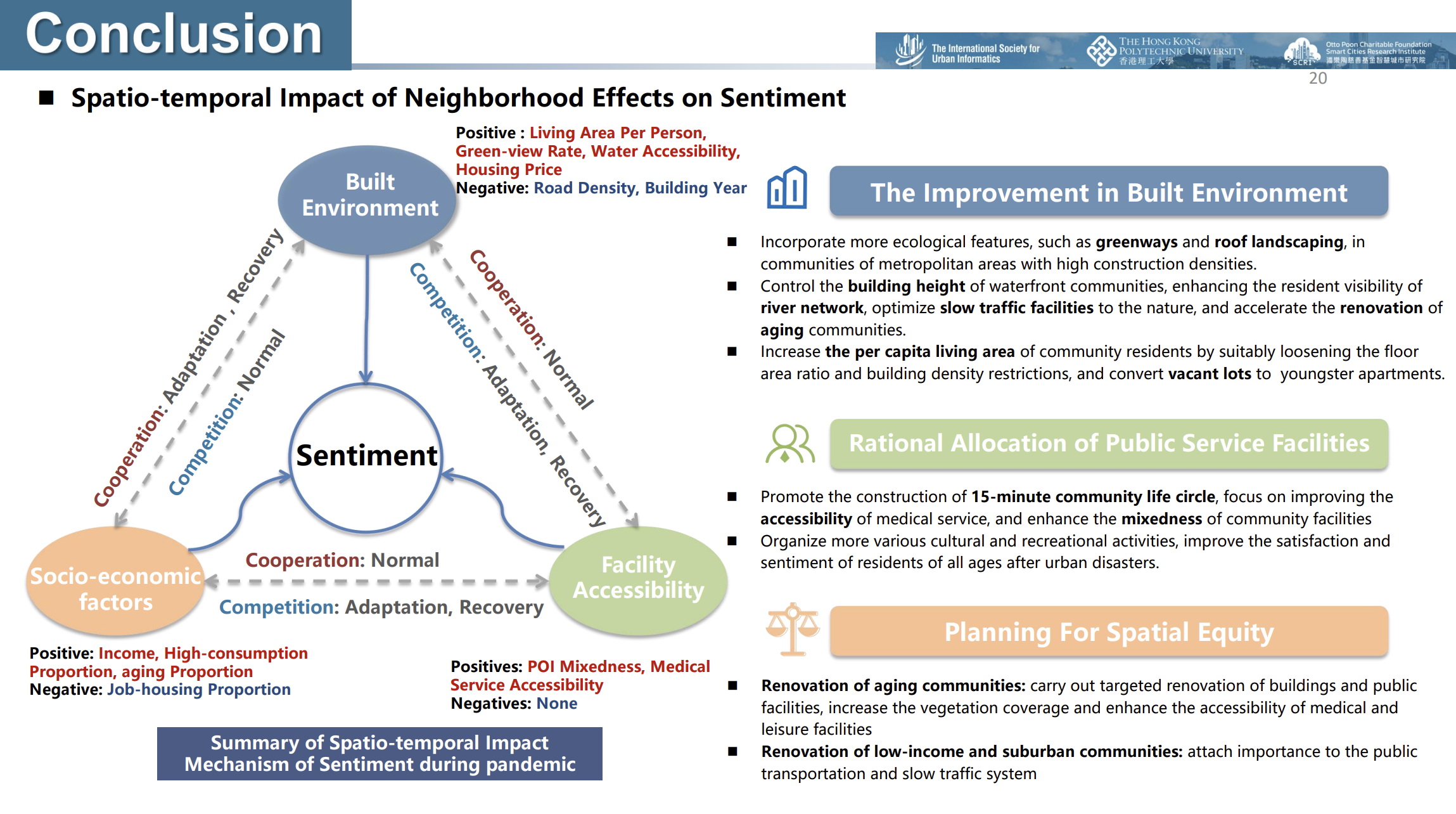
Associations between Socio-Environmental Dynamics and SWB
During the COVID-19 pandemic, urban residents' subjective well-being (SWB) was at risk, but few studies examined its relationship with neighborhood-level socio-economic and built-environment factors. This study bridges that gap by analyzing over one million geo-tagged social media posts from Shanghai.
Key contributions
- Utilized the ChatGPT API to analyze social media sentiment indices, combined with BerTopic to extract high-frequency topics, revealing the spatiotemporal dynamics of urban emotions during public disturbances.
- Used Regression Discontinuity Design (RDD) to divide the COVID-19 outbreak in Shanghai into six SWB stages, analyzing key events' impact on public sentiment before, during, and after the pandemic.
- Applied a Fully Connected Neural Network (FCNN) model to examine the relationship between sentiment scores and socio-economic as well as built-environment factors at the neighborhood level, with the SHAP framework used to explain the model.
The study found that green and blue spaces boost psychological resilience, while higher road density, attraction accessibility, and healthcare services reduce the link between sentiment, income, and aging. These insights inform urban planning and policy-making to enhance residents' resilience.
Honor: The First Prize in the 7th Chengyuan Cup; Best Presentation Award in GSCS & ICUI 2023; Submitted to the journal Computers, Environment and Urban Systems.
▶ NoiseLoc: campus noise monitoring and traceability system
June 01, 2021 – Nov 17, 2022
Keywords: noise traceability, sound classification and intensity prediction, interactive web app
Campus noise affects students and staff, and the noise tracing system provides precise analysis and decision-making support. This project uses GIS technology to create a multi-dimensional noise map, incorporating user feedback to identify noise sources. The interactive website features noise info, scenario distribution, event simulation, and source tracking.
Key technologies
- Employ a geometric acoustic ray tracing method to simulate noise propagation, accounting for reflection, diffraction, and atmospheric absorption, enabling accurate noise propagation calculations across different sources.
- Applied VGGish model and CNN network based on Short-Time Fourier Transform and mel-spectrogram features to classify and measure campus noise intensity.
- Developed the jarcpy module to replace ArcPy, combining shapely to re-implement functions like shape conversion, data statistics, distance calculation, and topology, improving compatibility and computational speed significantly in the Python3 environment.
Honor: The Grand Prize in the 1st 'Sky Cup' National College Students Spatial Information Technology Competition
